For Outstation Students, we are having online project classes both technical and coding using net-meeting software
For details, Call: 9886692401/9845166723
DHS Informatics providing latest 2021 – 2022 IEEE projects on Electrical projects for the final year engineering students.One of the leading final year project consultancy for CSE | ISE | ECE | EEE | Mechanical students in Bangalore, INDIA.
DHS Informatics trains all students in Electrical techniques to develop their project with good idea what they need to submit in college to get good marks. DHS Informatics offers placement training in Electrical at Bangalore and the program name is OJT – On Job Training, job seekers as well as final year college students can join in this placement training program and job opportunities in their dream IT companies. We are providing IEEE projects for B.E / B.TECH, M.TECH, MCA, BCA, DIPLOMA students from more than two decades.
Python Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
Abstract:
With the goal to decrease weight and increase overall efficiency, power electronics is proliferating in the aircraft applications. The conventional mechanical, pneumatic, and hydraulic systems are substituted with on-board electrical distribution systems. The new power electronics based distribution architectures should comply with the airworthiness standards by providing adequate redundancy to operate even under multiple failures. However, each redundant system adds to more weight and cost, and hence optimizing redundancy without compromising safety still remains a challenge. In this scenario, modular power converters offer a promising solution for obtaining reliable operation. Apart from ensuring availability and operation of the system, the modular converters enable controlling the stress for the individual converter cell and therefore their wear-out. This paper considers the failure mechanisms of the most sensitive devices in the system, the power semiconductors, and predicts their remaining useful lifetime (RUL). Based on this RUL, an optimization of the system loading is performed in order to delay the wear-out based failures in the system without reducing the mean lifetime of the building blocks. A study case is shown in order to demonstrate the lifetime extension of the system with the proposed algorithm
Abstract:
Equivalent power electronics converters (PECs), which have same performance characteristics but dissimilar configurations, are easily mistaken as different converters to be repeatedly studied in the practice, resulting in extra workload. Therefore, it is essential to implement the equivalence identification to avoid the undesired repeated research. In order to accomplish this goal, a computer-aided solution is proposed in this letter, aiming to quickly and precisely identify the equivalent PECs. First, two identification rules are figured out, with which different PECs can be systematically judged to be equivalent or not. Then, software Altium Designer is used to automatically acquire the information of PECs, including the components and the connecting relationships. After that, software MATLAB is utilized to further complete the data process, circuit loop search, and final judgment. Compared with the conventional manual identification method, which is totally dependent on researcher’s effort, the proposed computer-aided scheme is more convenient, accurate, and practical, which is beneficial for the topology research in both academic and industrial fields.
Abstract:
With the rapid development of the electric power grid and high-power tractions, megawatt power electronics technology is receiving tremendous attentions across the globe. The major obstacles to its further development still exist in enhancing its capability and reliability. Technical challenges and opportunities of megawatt power electronics are summarized first. It points out that the electromagnetic transient behaviors, especially at the short-timescales, are the main challenges. The transient behaviors of power electronics systems manifest themselves in the main-power loop, gate-drive loop, and control loop. After a detailed discussion of the transient behaviors, it is concluded that focusing on the multiscale transient behaviors can lead to significant overall performance improvement. A new perspective on the power electronics theory and techniques will lead to the development of a methodology for the analysis, design, and control of megawatt power electronics converters with significant improvements.
Abstract:
Megawatt power electronics is an enabling technology for many important industrial applications, including renewable power generation and integration, flexible electric power transmission and distribution, medium-voltage motor drives, and locomotive tractions. Major obstacles still exist for further enhancing its capability and reliability. Part I concluded that the transient behaviors are the key to megawatt power electronics systems designs for superior overall performance, low de-rating requirements and high reliability. This paper builds on the perspective of transient behaviors and presents some key techniques for the design and control of megawatt power electronics converters for high capability and reliability. The techniques include effective utilization of the state-of-art active devices and passive components with optimal power device selections, transient circuit topologies, and energy-balance-based control strategies. Practical application examples are presented to validate the proposed design techniques and to demonstrate their effectiveness.
Abstract:
Die attach by low-temperature silver sintering has been widely used in power electronics packaging. Most of the reported work was done on direct-bond-copper (DBC) substrates metallized with silver or gold. There is a lack of studies of sintered-silver bonding on nickel (Ni), a low-cost metallization on DBC. In this study, we fabricated a power module using pressureless in-air sintered-silver die attach on a Ni-plated DBC substrate. Strong die-shear strength of over 40 MPa was achieved. It was also found the static and switching characteristics, and the transient and steady-state thermal performance of the modules using Ni metallization was as good as that using Au metallization. Cross-sectional microstructure and chemistry analyses of the sintered-Ag/Ni interface revealed limited Ni oxidation. We believed that the high-density packing of silver particles and outgassing of the organic molecules from the paste during the bonding process helped to lower the partial pressure of oxygen in the bondline, which, in turn, prevented rapid Ni oxidation and gave rise to extensive formation of strong Ag-Ni metallic bonds at the interface. The findings of this study show the low-cost potential of the die-attach technology for power module packaging since the bonding process can be done pressureless in air on low-cost Ni metallization.
Abstract:
This paper presents a review of the electrical and electronic technologies investigated in more-electric aircraft (MEA). In order to change the current situation of low power efficiency, serious pollution, and high operating cost in conventional aircraft, the concept of MEA is proposed. By converting some hydraulic, mechanical, and pneumatic power sources into electrical ones, the overall power efficiency is greatly increased, and more flexible power regulation is achieved. The main components in an MEA power system are electrical machines and power electronics devices. The design and control methods for electrical machines and various topologies and control strategies for power electronic converters have been widely researched. Besides, several studies are carried out regarding energy management strategies that intend to optimize the operation of MEA power distribution systems. Furthermore, it is necessary to investigate the system stability and reliability issues in an MEA, since they are directly related to the safety of passengers. In terms of machine technologies, power electronics techniques, energy management strategies, and the system stability and reliability, a review is carried out for the contributions in the literature to MEA.
Abstract:
This letter proposes a novel wireless power transfer (WPT) system with repeater coils for multiple loads. Every two repeater coils form a repeater unit where one is used to receive power from its preceding unit and the other transmits power to the subsequent unit. Each load is connected to a repeater unit and multiple loads can be powered with several repeater units. The two coils in the same repeater unit are both bipolar ones, which are placed perpendicularly so that the magnetic coupling between them can be eliminated. In order to obtain independent power control of all the loads, the series-parallel-series compensation method is adopted for each repeater unit. With a proper resonant condition proposed in this letter, the constant load current can be obtained for all the loads when neglecting the coils’ parasitic resistances. An experimental setup has been constructed and the effectiveness of the proposed multi-load WPT system is validated by the experimental.
Abstract:
In order to correctly simulate the simultaneous switching of power electronics circuits and to solve the problems of virtual power loss existing in the traditional interpolation algorithm, this article proposes interpolation algorithm considering simultaneous solution and instantaneous solution. After each integration, it searches for he switching events and determines the simultaneous switching. The simultaneous switching events are solved simultaneously. Instantaneous solution is carried out at forced commutation switching instant. The historical terms calculation method in instantaneous solution under different conditions is given, and the exact power loss of forced commutation switch is obtained. After processing all switching events during one time-step, the half-step interpolation is performed to eliminate numerical oscillations. The proposed algorithm is applied to the electromagnetic transient programme of advanced digital power system simulator (ADPSS), and the correctness and effectiveness of the algorithm are verified by simulation tests for typical power electronics circuits. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has high simulation accuracy and can satisfy requirements of power electronics simulation.
Abstract:
Abstract:
Abstract:
Abstract:
Abstract: In order to correctly simulate the simultaneous switching of power electronics circuits and to solve the problems of virtual power loss existing in the traditional interpolation algorithm, this article proposes interpolation algorithm considering simultaneous solution and instantaneous solution. After each integration, it searches for he switching events and determines the simultaneous switching. The simultaneous switching events are solved simultaneously. Instantaneous solution is carried out at forced commutation switching instant. The historical terms calculation method in instantaneous solution under different conditions is given, and the exact power loss of forced commutation switch is obtained. After processing all switching events during one time-step, the half-step interpolation is performed to eliminate numerical oscillations. The proposed algorithm is applied to the electromagnetic transient programme of advanced digital power system simulator (ADPSS), and the correctness and effectiveness of the algorithm are verified by simulation tests for typical power electronics circuits. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has high simulation accuracy and can satisfy requirements of power electronics simulation.
Contact:
![]() +91-98451 66723
+91-98451 66723
![]() +91-98866 92401
+91-98866 92401
.
Abstarct : Photovoltaic (PV)/battery hybrid power units have attracted vast research interests in recent years. For the conventional distributed power generation systems with PV/battery hybrid power units, two independent power converters, including a unidirectional dc_dc converter and a bidirectional converter are normally required. This paper proposes an energy management and control strategy for the PV/battery hybrid distributed power generation systems with only one integrated three-port power converter. As the integrated bidirectional converter shares power switches with the full-bridge dc_dc converter, the power density and the reliability of the system is enhanced. The corresponding energy management and control strategy are proposed to realize the power balance among three ports in different operating scenarios, which comprehen- sively takes both the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) bene_t and the battery charging/discharging management into consideration. The simulations are conducted using the Matlab/Simulink software to verify the operation performance of the proposed PV/battery hybrid distributed power generation system with the corresponding control algorithms, where the MPPT control loop, the battery charging/discharging management loop are enabled accordingly in different operating scenarios.
Abstract – The situation, grid integration of variable renewable energy and electricity sector reforming in Japan, will increase uncertainties in power system operation.To handle these uncertainties, this paper introduces the sophisticated voltage and reactive power management technology based on AC-OPF (Optimal Power Flow) using online data, advanced online volt/var(Q) control system (OPENVQ: Optimized Performance Enabling Network for Volt/var(Q)), which can reduce operating expenditure (OPEX) by transmission loss reduction and optimized control of shunt devices and transformer taps, and/or capital expenditure (CAPEX) by optimized management of voltage control assets. Its architecture consists of a security assessment, a look-ahead operational condition predictor, optimal power flow calculation, and scenario analyzer. To validate the performance of OPENVQ system, a simulator has been developed that can handle multi-period operational conditions considering time series. Simulation results based on the TEPCO Power Grid 1500-bus model show that multiple control procedures created by OPENVQ system can optimize the KPIs, and new logic to reduce the number of control of shunt devices and transformer taps for managing grid voltage could be confirmed.Furthermore the feasibility study of OPENVQ system in Thailand has been conducted by NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization)’s study scheme in Japan.
Abstract : In the existing technique for power electronic converters with low switching frequency and multiple cells, the sampling frequency is always set at the same value as the control frequency, and the modulating wave in each cell updates itself when its corresponding carrier reaches its peak and valley. In this paper, this implementation scheme is denoted as AS-PWM. It is proved that AS-PWM suffers from three defects: further increase of switching frequency is restricted by the available control period and the total cell number; long modulator delay exists and may bring the control system into instability if high cross-over frequency is chosen; and spectrum aliasing towards digital modulating waves may occur and makes the ac input current distorted. Therefore, another implementation scheme of carrierbased digital PWM (DPWM) is recommended in this paper, which is denoted as MS-PWM. In MS-PWM, all of the modulating waves update themselves at the same time. The research presented in this paper is based on a power electronic traction transformer (PETT), which is made up of a cascaded H-bridge (CHB) converter and several DC/DC converters. For the consideration of scalability, control and reliability, a star-connected distributed control system is adopted for the PETT equipment. In order to make full use of this distributed hardware, and to improve the control performance with relatively low requirement towards the digital chips, a universal-type multirate structure is proposed in this paper, which is based on the MS-PWM technique. In the proposed structure, the sampling frequency, control frequency and modulating-wave updating frequency can be separated from the switching frequency, and each of them can be chosen independently according to the practical control demand and the hardware condition. There is no mutual effect between their selections. The influence of the variation of these three frequencies on the control performance is analyzed as well. At last, experiment results based on a five-cell PETT laboratory prototype with rated power of 30 kW are provided, and all of them verify the effectiveness and correctness of the proposed algorithms.
Abstract : The Congestion management of multi bus i.e 30 bus system is assessed by optimal sizing of PV system in this research paper. The recitation analysis of PV system has carried out in 30 bus system for the development of power system security through MATPOWER software. When the multi bus system goes an unexpected loading, its stability and security of the system is disturbed. It is required better results, it is required better the security from the disturbance of the areas. Here, the system is monitoring by continuation power flow (CPF), because of to improve the congestion situation of the systems. The various operating conditions like without PV system and with PV system tuned by Multi verse optimization algorithm. It has used to evaluate the performance of the proposed systems. The result shows, the system with PV system properly is tuned by this algorithm. It produces better result than the systems without PV.
A built-in digitalized power management (DPMM) and voltage domain programmable (VDP) mechanisms are proposed to design a low-power system. In the proposed techniques, the high and low voltages applied to logic modules can be switchable. This flexible voltage-domain assignment allows the chip performance and power consumption can dynamically adjust during circuit operation. To support the DPMM and VDP mechanisms, the voltage-level monitor circuit and power-switch circuit are designed to support multiple operation modes for DPMM-VDP digital circuit designs. A powerless retention flip-flop is developed for temporary data storage during voltage domain dynamically switching. While to prevent the system failure come from voltage integrity problem, a built-in voltage-level monitoring mechanism is utilized to monitor voltage integrity during VDP circuit operation. The proposed mechanism allows the chip performance and power consumption to be flexibly adjusted during circuit operation. The physical implementation chips and measured results proof of this methodology has 30~55% power reduction comparisons with using single-Vdd.
Abstract : One of the promising directions for finding solutions to the problems of regimes management and commercial electricity accounting in electric power systems is the application of distributed ledger technologies – Blockchain, which is due to increased availability of renewable energy sources. Currently, in the Russian Federation, the use of Blockchain technology is difficult for electric power systems operating in parallel with regional or unified power system due to the legislative restrictions imposed on operations in the retail and wholesale market for electrical energy. However, based on the distributed ledger technologies, the principles of the functioning of the electric energy market can be applied within the framework of small isolated electricity systems – microgrids. Mathematical modeling and calculation of the microgrid electric regimes were performed in the RastrWin3 program with the aim of accounting for losses in the electric power system. During the simulation it was obtained dependence of the power at the slack node from the number of load nodes for a different ratio of own generation to consumption in the node. In the case of positive power, there was a shortage of actual power in the system at the slack node, and in the case of a negative one, there was an excess of it. The use of distributed generation is economically justified in small isolated electricity system: the payback period of distributed generation devices is much less than their lifetime. It is possible to use Blockchain technology to organize mutual settlements between owners of small generation facilities in microgrid.
?
Abstract : Power electronics based Medium-Voltage Direct Current (MVDC) Microgrids consist of several interconnected feedback-controlled switching converters. Such systems experience bus voltage stability challenges owing to the negative incremental resistance of Constant Power Loads (CPLs) and converter control loop interactions. To tackle the stability challenges, this paper presents the application of the Interconnection and Damping Assignment Passivity Based Control (IDA-PBC) approach to the Port Controlled Hamiltonian (PCH) model of Dual Active Bridge (DAB) source-side converters in a MVDC Microgrid. For the DABs, a Fundamental Average Model (FAM) approach considering Phase Shift Modulation (PSM) is provided and used for deriving the corresponding IDA-PBC control law. We analyze the effectiveness of the controller on large signal scenarios considering disturbances such as load step up, and DAB disconnection. Hardware-in-the-Loop (HiL) experiments using Opal-RT and Labview FPGAs, as well as, low power prototype tests are carried out to demonstrate the validity and feasibility of the proposed approach.
Abstract : This paper presents a Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) application of the Custom Power Active Transformer (CPAT); a power electronics integrated transformer which provides services to the grid through its auxiliary windings. The CPAT structure integrates three single-phase transformers into one shunt-series combining transformer. This integration empowers a sub-station with the capability of dynamically regulating the terminal voltage and current of a transformer through isolated power electronics converters. This paper investigates the CPAT’s capability to provide UPFC services which includes power flow control, reactive power compensation, voltage regulation and harmonics elimination. Simulations of the CPAT-UPFC with a stiff grid and a 5-bus power system demonstrates its functionality as an inter-bus coupling transformer that provides the required grid services. Moreover, the impact of the CPAT-UPFC during load perturbations on the power system is investigated to further validate its transient and steady-state response. Furthermore, an experimental prototype reveals the operation of the three-phase CPAT-UPFC confirming its stable operation according to the theoretical expectations.
IEEE ELECTRICAL PROJECTS (2021 – 2022)
| S.NO | EEE/ELECTRICAL BASED PROJECTS | BASE PAPERS | TYPE |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
A Network-Based Approach for Modeling Resonant Capacitive Wireless Power Transfer Systems
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
2
|
Computer-Aided Identification of Equivalent Power Electronics Converters
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
3
|
A Multi-load Wireless Power Transfer System with Series-parallel-series (SPS) Compensation
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
4
|
Design and Optimization of a Solar Power Conversion System for Space Applications
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
5
|
A Unified Power Flow Controller Using a Power Electronics Integrated Transformer
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
6
|
Research on AC & DC hybrid power supply system with high-proportion renewable energy of data centre
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
7
|
A Comprehensive Review of Maritime Microgrids: System Architectures, Energy Efficiency, Power Quality, and Regulations
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
8
|
Electrical and Electronic Technologies in More-Electric Aircraft: A Review
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
9
|
Interpolation algorithm considering simultaneous solution and instantaneous solution for power electronics electromagnetic transient simulation
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
10
|
Improving Onboard Converter Reliability For More Electric Aircraft With Lifetime-based Control
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
11
|
Mitigation of Interharmonics in PV Systems with Maximum Power Point Tracking Modification
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
12
|
Pressureless Silver Sintering on Nickel for Power Module Packaging
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
13
|
Carrier-Based Digital PWM and Multirate Technique of a Cascaded H-Bridge Converter for Power Electronic Traction Transformers
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
14
|
Transient Behaviors of Multiscale Megawatt Power Electronics Systems—Part I:Characteristics and Analysis
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
15
|
Transient Behaviors of Multiscale Megawatt Power Electronics Systems—Part II: Design Techniques and Practical Applications
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
16
|
A Review of Gallium Nitride Power Device and Its Applications in Motor Drive
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
17
|
Review of Power Conversion and Energy Management for Low-Power,Low-Voltage Energy Harvesting Powered Wireless Sensors
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
18
|
Current-Sensorless Power Factor Correction With Predictive Controllers
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
19
|
Systematic Reliability Modeling and Evaluation for On-Board POWER ELECTRONICSs of More Electric Aircrafts
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
20
|
Direct Power Control Method With Minimum Reactive Power Reference for Three-Phase AC-to-DC Matrix Rectifiers Using Space Vector Modulation
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
21
|
Energy Management and Control Strategy of Photovoltaic/Battery Hybrid Distributed Power Generation Systems With an Integrated Three-Port Power Converter
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
22
|
Design and Experiment of a High Average Power Ku-Band TE01 Mode Gyro-TWT
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
23
|
Collaborative unbalance compensation method for high-speed railway traction power supply system considering energy feedback
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
24
|
Predictive Power Control for DFIG: A FARE-Based Weighting Matrices Approach
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
25
|
Auxiliary Power Supply for Medium-Voltage Power Converters: Topology and Control
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
26
|
Optimal Phase-Shift Control to Minimize Reactive Power for a Dual Active Bridge DC–DC Converter
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
27
|
Multivariable High-Frequency Input-Admittance of Grid-Connected Converters: Modeling, Validation, and Implications on Stability
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
28
|
Measurement of Lightning-Induced Overvoltage in Power Distribution Lines Using Ceramic-Capacitor Insulator
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
29
|
Gate-driver circuit with a variable supply voltage to influence the switching losses
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
30
|
Fully Implantable Cochlear Implant Interface Electronics With 51.2- μ W Front-End Circuit
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
31
|
An Efficient Power Management Circuit Based on Quasi Maximum Power Point Tracking With Bidirectional Intermittent Adjustment for Vibration Energy Harvesting
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
32
|
Multi-frequency power system for renewable source integration in smart grid
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
33
|
Time Domain Analysis of Reactive Components and Optimal Modulation for Isolated Dual Active Bridge DC/DC Converters
|
POWER ELECTRONICS
|
|
|
34
|
Virtual power plant energy optimisation in smart grids
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
35
|
One-day ahead predictive management of building hybrid power system improving energy cost and batteries lifetime
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
36
|
Stochastic Multi-objective Economic/Emission Energy Management of a Microgrid in Presence of Combined Heat and Power Systems
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
37
|
Energy Management and Control Strategy of Photovoltaic/Battery Hybrid Distributed Power Generation Systems With an Integrated Three-Port Power Converter |
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
38
|
Design and Implementation of a Fully Controllable Cyber-Physical System for Testing Energy Storage Systems
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
39
|
Innovative Practice of Line Loss Management Model Based on Big Data
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
40
|
An Ultra-Low Power Multi-Level Power-on Reset for Fine-Grained Power Management Strategies
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
41
|
Advanced Online Volt/var(Q) Control System for Optimal Voltage Profile
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
42
|
Hybrid PEM Fuel-Cell-Solar Power System Design for Electric Boat with MPPT System and Fuzzy Energy Management
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
43
|
Impact of Renewable Energies Integration in Interconnected Power System: Transmission-Distribution
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
44
|
Microgrid Energy Management System for Reducing Required Power Reserves
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
45
|
Asset Performance Enhancement Initiatives on Major Switchgears and Transformers in CLP Power Hong Kong
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
46
|
Congestion Management based Optimal Sizing of PV System using MultiVerse Optimization Algorithm
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
47
|
Economic Operation Platform for Power Grid Company
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
48
|
Energy Storage System Application in MEA Building
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
49
|
Digitalized-Management Voltage-Domain Programmable Mechanisms for Dual-Vdd Low-Power Embedded Digital Systems
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
50
|
The Improvement of «Management of Nonconformities and Corrective Actions” Process in the Design of the Power Supply System of Tram Lines
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
51
|
Review of Power Conversion and Energy Management for Low-Power,Low-Voltage Energy Harvesting Powered Wireless Sensors
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
52
|
Automated Integration of Dynamic Power Management into FPGA-Based Design
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
53
|
Architecture Design of Communication and Backhaul for UAVs in Power Emergency Communication
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
54
|
An Ordered Curtailment Strategy for Offshore Wind Power Under Extreme Weather Conditions Considering the Resilience of the Grid
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
55
|
Hybrid Access in Storage-class Memory-aware Low Power Virtual Memory System
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
56
|
Research on Wide-area Distributed Power Quality Data Fusion Technology of Power Grid
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
57
|
Predictive Control of Flexible Resources for Demand Response in Active Distribution Networks
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
58
|
A Novel Multi-mode Electric Power Emergency Communication System
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
59
|
Dynamic load-shedding for enhancement of power system stability for the Lesotho 132 kV transmission network
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
60
|
Study of Coordinated Reactive Power Control for Distribution Grid Voltage Regulation with Photovoltaic Systems
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
61
|
Electrical and Electronic Technologies in More-Electric Aircraft: A Review
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
62
|
Application of micro-grid control system in smart park
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
63
|
Impact of Control Systems on Power Quality at Common DC Bus in DC Grid
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
64
|
Integrated Control of Renewable Energy and Fault Restoration for Distribution Systems
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
65
|
Total Harmonics Distortion (THD) with PV System Integration in Smart Grids: Case Study
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
66
|
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Emergency Power Upgrades in Critical Facilities
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
67
|
Modified Power Reserve Management Solution in Power System Considering Frequency Constraints
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
68
|
Research on Linkage Model of Network Resource Survey and Vulnerability Detection in Power Information System
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
69
|
A Review of Power System Flexibility With High Penetration of Renewables
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
|
|
70
|
Day-ahead scheduling of integrated electricity and district heating system with an aggregated model of buildings for wind power accommodation
|
POWER SYSTEMS
|
DHS Informatics believes in students’ stratification, we first brief the students about the technologies and type of Electrical projects and other domain projects. After complete concept explanation of the IEEE Electrical projects, students are allowed to choose more than one IEEE Electrical projects for functionality details. Even students can pick one project topic from Electrical and another two from other domains like Electrical, image process, information forensic, big data, and Electrical, block chain etc. DHS Informatics is a pioneer institute in Bangalore / Bengaluru; we are supporting project works for other institute all over India. We are the leading final year project centre in Bangalore / Bengaluru and having office in five different main locations Jayanagar, Yelahanka, Vijayanagar, RT Nagar & Indiranagar.
We allow the ECE, CSE, ISE final year students to use the lab and assist them in project development work; even we encourage students to get their own idea to develop their final year projects for their college submission.
DHS Informatics first train students on project related topics then students are entering into practical sessions. We have well equipped lab set-up, experienced faculties those who are working in our client projects and friendly student coordinator to assist the students in their college project works.
We appreciated by students for our Latest IEEE projects & concepts on final year Electrical projects for ECE, CSE, and ISE departments.
Latest IEEE 2021 – 2022 Electrical Engineering Projects on Electrical with real time concepts which are implemented using Java, MATLAB, and NS2 with innovative ideas. Final year students of computer Electrical, computer science, information science, electronics and communication can contact our corporate office located at Jayanagar, Bangalore for Electrical project details.
ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS

Embedded systems are a cornerstone of the electronics industry today.
An embedded system is a computer or processor based system that has been designed for a specific purpose.
The system gains its name from the fact that the software is embedded into it for a particular application. The embedded system is not like a PC or other computer that can run a variety of programmes and fulfil a whole host of tasks.
The item using an embedded system is designed for a specific task and has its software preloaded, although updates may be undertaken from time to time.
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS BASICS
It may be asked what is an embedded system. With many processor based systems and computers it is useful to define what an embedded system is. A convenient definition for an embedded system is An embedded system is any computer system contained within a product that is not described as a computer.
Using this embedded system definition it is possible to understand the various basic characteristics one. Typically they are:
- Embedded systems are designed for a specific task. Although they use computer techniques, they cannot be used as a general purpose computer using a variety of different programmes for different task. In this way their function can be focussed onto what they need to do, and they can accordingly be made cheaper and more efficiently.
- The software for embedded systems is normally referred to as firmware. Rather than being stored on a disc, where many programmes can be stored, the single programme for an embedded system is normally stored on chip and it is referred to as firmware.
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS CONTAIN TWO MAIN ELEMENTS
- Embedded system hardware: As with any electronic system, an embedded system requires a hardware platform on which to run. The hardware will be based around a microprocessor or microcontroller. The embedded system hardware will also contain other elements including memory, input output (I/O) interfaces as well as the user interface, and the display.
- Embedded system software: The embedded system software is written to perform a particular function. It is typically written in a high level format and then compiled down to provide code that can be lodged within a non-volatile memory within the hardware.
EMBEDDED PROCESSOR HARDWARE
- Embedded systems basics
- Embedded processor hardware
- CPU
- Embedded MPU
- Embedded MCU
- RAM
When developing an embedded system, one of the options is to base the computational hardware around a microcontroller, MCU rather than a microprocessor, MPU.
Both approaches have their attractions, but generally they will be found in different applications. Typically the microcontroller, MCU, is found in applications where size, low power and low cost are key requirements.
The MCU, microcontroller is different to a microprocessor in that it contains more elements of the overall processing engine within the one chip.
Bringing most of the processing engine components onto a single chip reduces size and cost. This enables it to become economical viable to digitally control even more devices and processes. Also it is found that mixed signal microcontrollers are being increasingly used, integrating analogue components needed to control non-digital electronic systems.
MICROCONTROLLER BASICS
Microcontrollers comprise the main elements of a small computer system on a single chip. They contain the memory, and IO as well as the CPU one the same chip. This considerably reduces the size, making them ideal for small embedded systems, but means that there are compromises in terms of performance and flexibility.
As microcontrollers are often intended for low power and low processing applications, some microcontrollers may only use 4 bit words and they may also operate with very low clock rates – some 10 kHz and less to conserve power. This means that some MCUs may only consume a milli watt or so and they may also have sleep consumption levels of a few nano watts. At the other end of the scale some MCUs may need much higher levels of performance and may have very much higher clock speeds and power consumption.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF MICROCONTROLLERS
- 8051
- ARM
- PIC
- Arduino
- AVR
| Functions | 8051 | PIC | AVR | ARM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bus width | 8-bit for standard core | 8/16/32-bit | 8/32-bit | 32-bit mostly also available in 64-bit |
| Communication Protocols | UART, USART,SPI,I2C | PIC, UART, USART, LIN, CAN, Ethernet, SPI, I2S | UART, USART, SPI, I2C, (special purpose AVR support CAN, USB, Ethernet) | UART, USART, LIN, I2C, SPI, CAN, USB, Ethernet, I2S, DSP, SAI (serial audio interface), IrDA |
| Speed | 12 Clock/instruction cycle | 4 Clock/instruction cycle | 1 clock/ instruction cycle | 1 clock/ instruction cycle |
| Memory | ROM, SRAM, FLASH | SRAM, FLASH | Flash, SRAM, EEPROM | Flash, SDRAM, EEPROM |
| ISA | CLSC | Some feature of RISC | RISC | RISC |
| Memory Architecture | Von Neumann architecture | Harvard architecture | Modified | Modified Harvard architecture |
| Power Consumption | Average | Low | Low | Low |
| Families | 8051 variants | PIC16,PIC17, PIC18, PIC24, PIC32 | Tiny, Atmega, Xmega, special purpose AVR | ARMv4,5,6,7 and series |
| Community | Vast | Very Good | Very Good | Vast |
| Manufacturer | NXP, Atmel, Silicon Labs, Dallas, Cyprus, Infineon, etc. | Microchip Average | Atmel | Apple, Nvidia, Qualcomm, Samsung Electronics, and TI etc. |
| Cost (as compared to features provide) | Very Low | Average | Average | Low |
| Other Feature | Known for its Standard | Cheap | Cheap, effective | High speed operation Vast |
| Popular Microcontrollers | AT89C51, P89v51, etc. | PIC18fXX8, PIC16f88X, PIC32MXX | Atmega8, 16, 32, Arduino Community | LPC2148, ARM Cortex-M0 to ARM Cortex-M7, etc. |

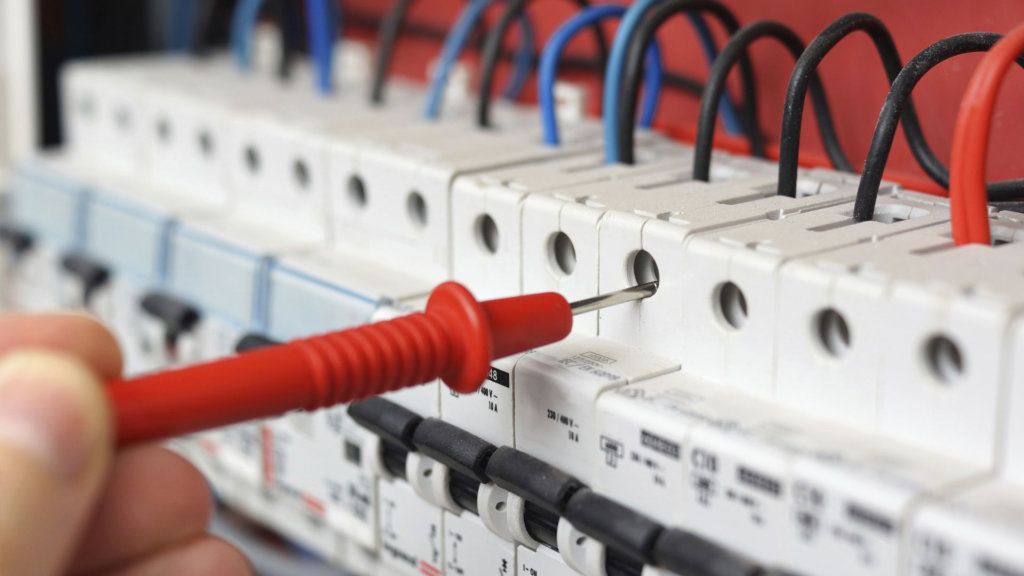
Final year EEE 2021 – 2022 IEEE BE/B-Tech projects | final year electrical engineering projects |Final Year EEE Projects| Electrical Engineering projects| Academic 2021 – 2022 Electrical Engineering projects |Final year EEE Projects|Final Year EEE Projects|Final Year EEE Projects|Electrical Engineering projects
Java Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
- Java Information Forensic / Block Chain B.E Projects
- Java Cloud Computing B.E Projects
- Java Big Data with Hadoop B.E Projects
- Java Networking & Network Security B.E Projects
- Java Data Mining / Web Mining / Cyber Security B.E Projects
- Java DataScience / Machine Learning B.E Projects
- Java Artificaial Inteligence B.E Projects
- Java Wireless Sensor Network B.E Projects
- Java Distributed & Parallel Networking B.E Projects
- Java Mobile Computing B.E Projects
Android Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
- Android GPS, GSM, Bluetooth & GPRS B.E Projects
- Android Embedded System Application Projetcs for B.E
- Android Database Applications Projects for B.E Students
- Android Cloud Computing Projects for Final Year B.E Students
- Android Surveillance Applications B.E Projects
- Android Medical Applications Projects for B.E
Embedded Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
- Embedded Robotics Projects for M.tech Final Year Students
- Embedded IEEE Internet of Things Projects for B.E Students
- Embedded Raspberry PI Projects for B.E Final Year Students
- Embedded Automotive Projects for Final Year B.E Students
- Embedded Biomedical Projects for B.E Final Year Students
- Embedded Biometric Projects for B.E Final Year Students
- Embedded Security Projects for B.E Final Year
MatLab Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
- Matlab Image Processing Projects for B.E Students
- MatLab Wireless Communication B.E Projects
- MatLab Communication Systems B.E Projects
- MatLab Power Electronics Projects for B.E Students
- MatLab Signal Processing Projects for B.E
- MatLab Geo Science & Remote Sensors B.E Projects
- MatLab Biomedical Projects for B.E Students