DHS Informatics providing latest 2024 – 2025 IEEE projects on Embedded IoT projects for the final year engineering students. DHS Informatics trains all students in IoT techniques to develop their Embedded system projects with good idea what they need to submit in college to get good marks. DHS Informatics offers placement training in IoT & Embedded System at Bangalore and the program name is OJT – On Job Training, job seekers as well as final year college students can join in this placement training program and job opportunities in their dream IT companies. We are providing IEEE projects for B.E / B.TECH, M.TECH, MCA, BCA, DIPLOMA students from more than two decades.
Python Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
IEEE EMBEDDED IOT PROJECTS (2022- 2023)
DHS Informatics believes in students’ stratification, we first brief the students about the technologies and type of Embedded IoT projects and other domain projects. After complete concept explanation of the IEEE Embedded IoT projects, students are allowed to choose more than one IEEE Embedded IoT projects for functionality details. Even students can pick one project topic from Embedded IoT and another two from other domains like Embedded IoT, image process, information forensic, big data, and Embedded IoT, block chain etc. DHS Informatics is a pioneer institute in Bangalore / Bengaluru; we are supporting project works for other institute all over India. We are the leading final year project centre in Bangalore / Bengaluru and having office in five different main locations Jayanagar, Yelahanka, Vijayanagar, RT Nagar & Indiranagar.
We allow the ECE, CSE, ISE final year students to use the lab and assist them in project development work; even we encourage students to get their own idea to develop their final year projects for their college submission.
DHS Informatics first train students on project related topics then students are entering into practical sessions. We have well equipped lab set-up, experienced faculties those who are working in our client projects and friendly student coordinator to assist the students in their college project works.
We appreciated by students for our Latest IEEE projects & concepts on final year Embedded IoT projects for ECE, CSE, and ISE departments.
Latest IEEE 2024 – 2025 projects on Embedded IoT with real time concepts which are implemented using Java, MATLAB, and NS2 with innovative ideas. Final year students of computer Embedded IoT, computer science, information science, electronics and communication can contact our corporate office located at Jayanagar, Bangalore for Embedded IoT project details.
EMBEDDED TECHNOLOGY AND IOT

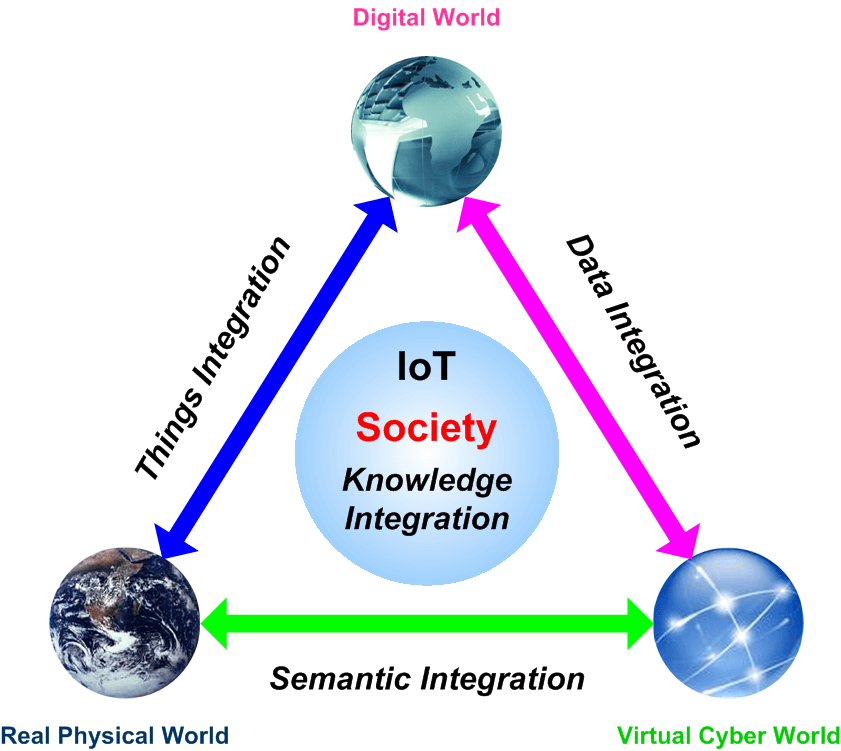
IoT (Internet of Things) is an advanced automation and analytics system which exploits networking, sensing, big data, and artificial intelligence technology to deliver complete systems for a product or service. These systems allow greater transparency, control, and performance when applied to any industry or system.
IoT systems have applications across industries through their unique flexibility and ability to be suitable in any environment. They enhance data collection, automation, operations, and much more through smart devices and powerful enabling technology.
IoT systems allow users to achieve deeper automation, analysis, and integration within a system. They improve the reach of these areas and their accuracy. IoT utilizes existing and emerging technology for sensing, networking, and robotics.
IoT exploits recent advances in software, falling hardware prices, and modern attitudes towards technology. Its new and advanced elements bring major changes in the delivery of products, goods, and services; and the social, economic, and political impact of those changes.
Here we provided a IOT/INTERNET things 2024 – 2025 project list with abstract/ABSTRACT. IOT has been a very hot active during past few years and holds the potential as yet largely untapped to allow decision makers to track development progress using latest concepts.
Latest IOT/INTERNET topics,Latest IOT/INTERNET concept for diplomo,Engineering students,IOT/INTERNET project centers in Bangalore with high quality training and development.
IOT FEATURES
- The most important features of IoT include artificial intelligence, connectivity, sensors, active engagement, and small device use. A brief review of these features is given below :−
- AIIoT essentially makes virtually anything “smart”, meaning it enhances every aspect of life with the power of data collection, artificial intelligence algorithms, and networks. This can mean something as simple as enhancing your refrigerator and cabinets to detect when milk and your favorite cereal run low, and to then place an order with your preferred grocer.
- ConnectivityNew enabling technologies for networking, and specifically IoT networking, mean networks are no longer exclusively tied to major providers. Networks can exist on a much smaller and cheaper scale while still being practical. IoT creates these small networks between its system devices.
- SensorsIoT loses its distinction without sensors. They act as defining instruments which transform IoT from a standard passive network of devices into an active system capable of real-world integration.
- Active EngagementMuch of today’s interaction with connected technology happens through passive engagement. IoT introduces a new paradigm for active content, product, or service engagement.
- Small Devices
Devices, as predicted, have become smaller, cheaper, and more powerful over time. IoT exploits purpose-built small devices to deliver its precision, scalability, and versatility.
IOT ADVANTAGE
- The advantages of IoT span across every area of lifestyle and business. Here is a list of some of the advantages that IoT has to offer :− Improved Customer Engagement Current analytics suffer from blind-spots and significant flaws in accuracy; and as noted, engagement remains passive. IoT completely transforms this to achieve richer and more effective engagement with audience.

IOT SOFTWARE
IoT software addresses its key areas of networking and action through platforms, embedded systems, partner systems, and middleware. These individual and master applications are responsible for data collection, device integration, real-time analytics, and application and process extension within the IoT network. They exploit integration with critical business systems (e.g., ordering systems, robotics, scheduling, and more) in the execution of related tasks.
-
- Data CollectionThis software manages sensing, measurements, light data filtering, light data security, and aggregation of data. It uses certain protocols to aid sensors in connecting with real-time, machine-to-machine networks. Then it collects data from multiple devices and distributes it in accordance with settings. It also works in reverse by distributing data over devices. The system eventually transmits all collected data to a central server.
- Device IntegrationSoftware supporting integration binds (dependent relationships) all system devices to create the body of the IoT system. It ensures the necessary cooperation and stable networking between devices. These applications are the defining software technology of the IoT network because without them, it is not an IoT system. They manage the various applications, protocols, and limitations of each device to allow communication.
- Real-Time Analytics
These applications take data or input from various devices and convert it into viable actions or clear patterns for human analysis. They analyze information based on various settings and designs in order to perform automation-related tasks or provide the data required by industry.
- Application and Process ExtensionThese applications extend the reach of existing systems and software to allow a wider, more effective system. They integrate predefined devices for specific purposes such as allowing certain mobile devices or engineering instruments access. It supports improved productivity and more accurate data collection.
IOT TECHNOLOGY AND PROTOCOLS
IoT primarily exploits standard protocols and networking technologies. However, the major enabling technologies and protocols of IoT are RFID, NFC, low-energy Bluetooth, low-energy wireless, low-energy radio protocols, LTE-A, and WiFi-Direct. These technologies support the specific networking functionality needed in an IoT system in contrast to a standard uniform network of common systems.
- NFC and RFID: RFID (radio-frequency identification) and NFC (near-field communication) provide simple, lowenergy, and versatile options for identity and access tokens, connection bootstrapping, and payments
- RFID technology employs 2-way radio transmitter-receivers to identify and track tags associated with objects.
- NFC consists of communication protocols for electronic devices, typically a mobile device and a standard device.
- Low-Energy Bluetooth: This technology supports the low-power, long-use need of IoT function while exploiting a standard technology with native support across systems.
- Low-Energy Wireless: This technology replaces the most power hungry aspect of an IoT system. Though sensors and other elements can power down over long periods, communication links (i.e., wireless) must remain in listening mode. Low-energy wireless not only reduces consumption, but also extends the life of the device through less use.
- Radio Protocols: ZigBee, Z-Wave, and Thread are radio protocols for creating low-rate private area networks. These technologies are low-power, but offer high throughput unlike many similar options. This increases the power of small local device networks without the typical costs.
- LTE-A : LTE-A, or LTE Advanced, delivers an important upgrade to LTE technology by increasing not only its coverage, but also reducing its latency and raising its throughput. It gives IoT a tremendous power through expanding its range, with its most significant applications being vehicle, UAV, and similar communication.
- WiFi-Direct: WiFi-Direct eliminates the need for an access point. It allows P2P (peer-to-peer) connections with the speed of WiFi, but with lower latency. WiFi-Direct eliminates an element of a network that often bogs it down, and it does not compromise on speed or throughput.
IEEE projects for CSE final year 2021-2022
Java Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
- Java Information Forensic / Block Chain B.E Projects
- Java Cloud Computing B.E Projects
- Java Big Data with Hadoop B.E Projects
- Java Networking & Network Security B.E Projects
- Java Data Mining / Web Mining / Cyber Security B.E Projects
- Java DataScience / Machine Learning B.E Projects
- Java Artificaial Inteligence B.E Projects
- Java Wireless Sensor Network B.E Projects
- Java Distributed & Parallel Networking B.E Projects
- Java Mobile Computing B.E Projects
Android Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
- Android GPS, GSM, Bluetooth & GPRS B.E Projects
- Android Embedded System Application Projetcs for B.E
- Android Database Applications Projects for B.E Students
- Android Cloud Computing Projects for Final Year B.E Students
- Android Surveillance Applications B.E Projects
- Android Medical Applications Projects for B.E

Embedded Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
- Embedded Robotics Projects for M.tech Final Year Students
- Embedded IEEE Internet of Things Projects for B.E Students
- Embedded Raspberry PI Projects for B.E Final Year Students
- Embedded Automotive Projects for Final Year B.E Students
- Embedded Biomedical Projects for B.E Final Year Students
- Embedded Biometric Projects for B.E Final Year Students
- Embedded Security Projects for B.E Final Year
MatLab Final year CSE projects in Bangalore
- Matlab Image Processing Projects for B.E Students
- MatLab Wireless Communication B.E Projects
- MatLab Communication Systems B.E Projects
- MatLab Power Electronics Projects for B.E Students
- MatLab Signal Processing Projects for B.E
- MatLab Geo Science & Remote Sensors B.E Projects
- MatLab Biomedical Projects for B.E Students